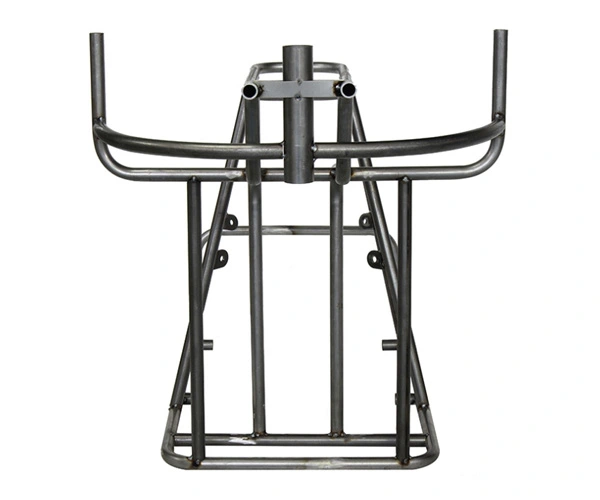
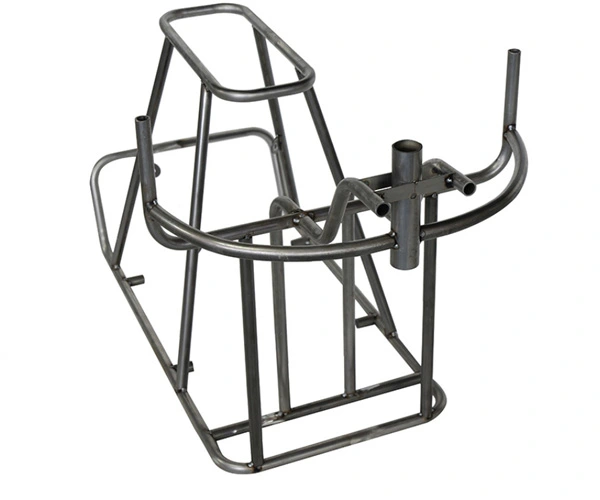
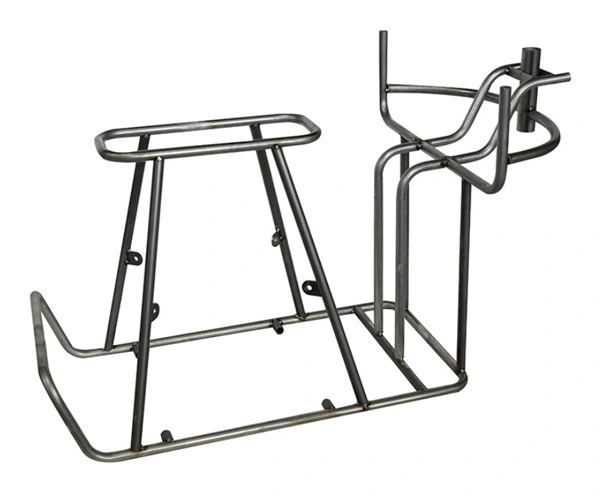
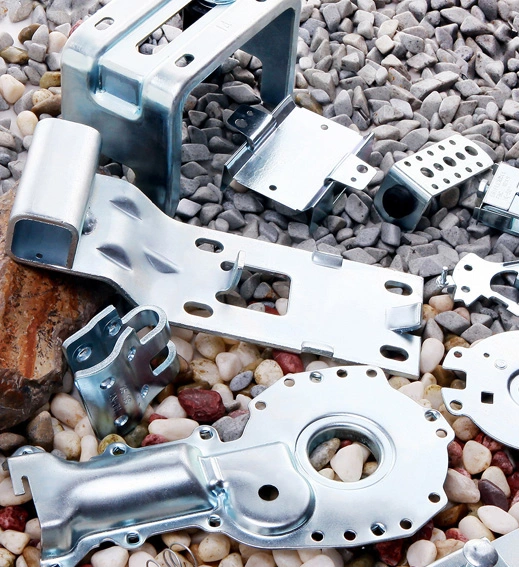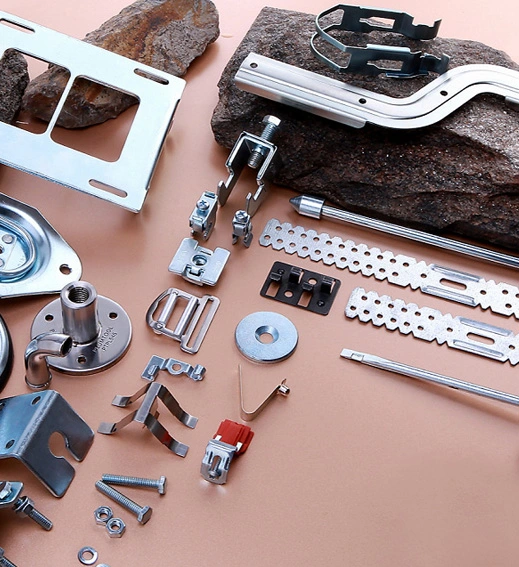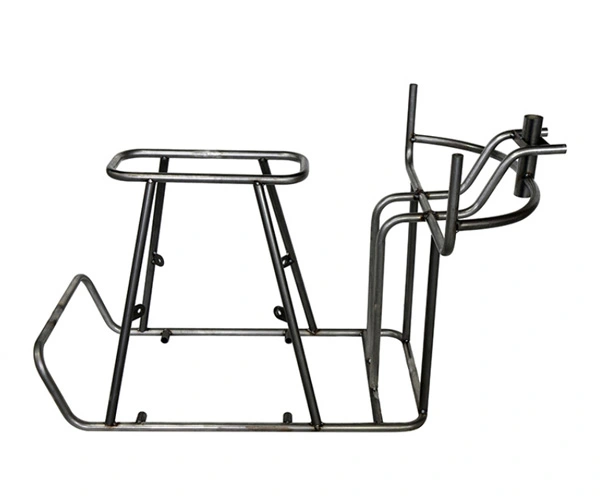

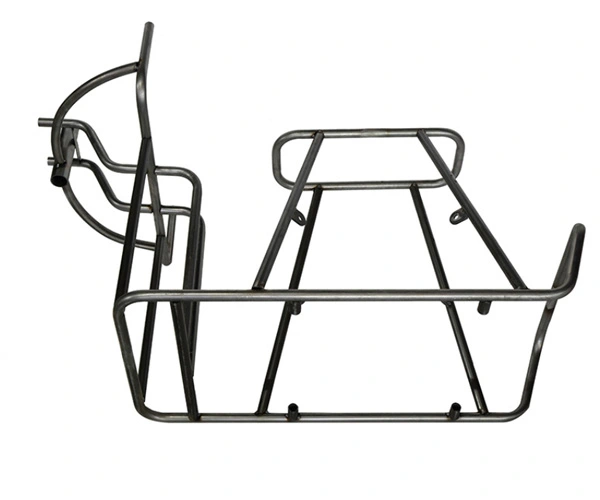







Material: Carbon steel
Surface: Mill finish
Customized Size
Main Process: bending and welding
Tolerance: ±0.25 mm
Stainless steel pipe, iron pipe, motorcycle guard bar, electric frame bending machining
Defects that do not meet the standard requirements during the welding process.
Due to the influence of factors such as human, machine, material, method, and environment, defects may occur inside and outside the weld seam, including: weld size not meeting the requirements, arc pits, burn through, undercutting, weld overlap, severe splashing, slag inclusion, porosity, cracks, etc.
During the welding process, the gas in the molten pool metal cannot escape before the metal cools down, and the pores formed in the weld metal (inside or on the surface).
The cracks formed in the weld metal and heat affected zone (internal or surface) under the combined action of welding stress and other brittle factors are called cracks Hot crack - a crack that occurs immediately after welding at high temperatures Cold crack refers to the crack that occurs when the metal is cooled to room temperature after welding; Cracks that occur a few hours or days after welding are called delayed cracks.
Due to incorrect selection of welding parameters or incorrect operation methods, grooves or depressions along the base metal of the weld toe (fusion line), called undercuts, can cause local stress concentration.
The phenomenon of incomplete fusion at the root of the joint during welding.
During fusion welding, the part between the weld bead and the base metal or between the weld bead and the weld bead that has not been completely melted and bonded.
Hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, three harmful gases, can cause great harm to welded joints; Especially hydrogen can cause hazards such as hydrogen pores, hydrogen white spots, hydrogen embrittlement, and hydrogen induced cracking (delayed cracking).
The phenomenon of molten metal particles and slag flying around during the welding process.
During the welding process, molten metal flows onto the unmelted base material outside the weld seam, forming a metal lump.
The phenomenon of residual welding slag in the weld seam.
When welding the arc, a depression is formed at the end of the weld bead that is lower than the height of the weld seam - called an arc crater. There are generally defects such as low melting point eutectic, inclusions, and flame cracks in the arc crater. Using the arc current (less than 60% of the welding current) to stay in the arc pit for a certain period of time and filling the arc pit with welding wire can prevent the occurrence of arc pit defects.



